Microsoft Windows Server LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel)
Microsoft Windows Server LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel) is a servicing option for Microsoft's server operating system that follows the familiar track of two to three years between feature updates.
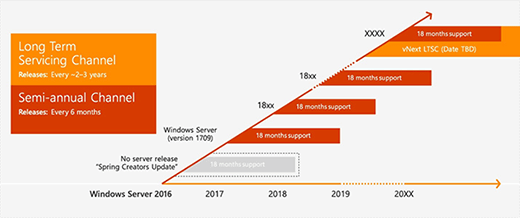
In June 2017, Microsoft announced it would split Windows Server into two channels: the Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) and the Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) -- formerly the Long-Term Servicing Branch. The SAC caters to enterprises that prefer a shorter term between feature updates to get the most recent updates for rapid application development cycles.
Microsoft tailors the LTSC for companies that prefer the more traditional release cycle of two to three years between major feature updates. The LTSC naming convention will retain the Windows Server YYYY format while the SAC releases will follow a Windows Server version YYMM format. Microsoft said it plans to add most of the enhancements -- with some variations -- from the SAC releases into upcoming LTSC releases.
LTSC installation options and support terms
The LTSC is available in two installation options: Server Core and Server with Desktop Experience mode, which provides a GUI for point-and-click management. Server Core has no GUI and requires the use of a remote server management tool. Microsoft's documentation also states Nano Server is available as a container OS on the LTSC platform.
While the SAC release of Windows Server that came out in October 2017 called Windows Server version 1709 also has Server Core, it is not compatible with the LTSC Server Core version. Administrators cannot upgrade LTSC Server Core to SAC Server Core because the support terms and channels are different. Similarly, there is no ability to change from LTSC Server Core to a LTSC Server with Desktop Experience deployment. The administrator needs to do a fresh install of each option.
Windows Server LTSC comes in three editions -- Essential, Standard and Datacenter -- and is available through all channels. The support terms will be familiar to most administrators with five years of mainstream support with five years of extended support. Enterprises also have the option for six additional years of support through Microsoft's Premium Assurance plan.
Availability of Windows Server preview releases
For enterprises that want to get an early look at the upcoming features in the next LTSC release, Microsoft makes preview builds available in its Windows Insider Program. Administrators can deploy these releases in a test environment to head off potential issues and see what features they can implement when Microsoft delivers the official release. Microsoft encourages customers to provide feedback during this testing phase to help shape the course of the LTSC release.







